Question
- Leaving Certificate Chemistry (Higher) 2020: Section B Q8
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
(i) Substitution = 4
(ii) Addition reaction = 6 and 5
(iii) Elimination reaction = 2 and 7
(b)
(i) H2/Ni
(ii)
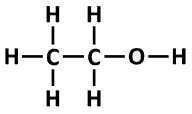
Bonds formed: C-H, C-C, C-O, O-H
(c) Ethanol is highly soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding.
(d)
(i) Compound X: Chloroethene
(ii) In conversion 7 the geometry changes from tetrahedral geometry to planar geometry due to the double bond.
(iii) Two repeating units of PVC
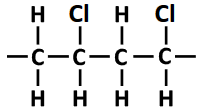
(e) Conversion 6 is an addition reaction.
Step 1: Polarisation — as the Cl2 moves towards the double bond of ethene it becomes polarised.
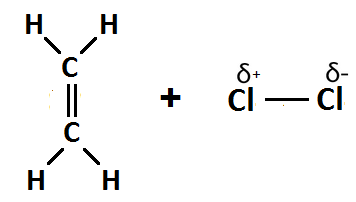
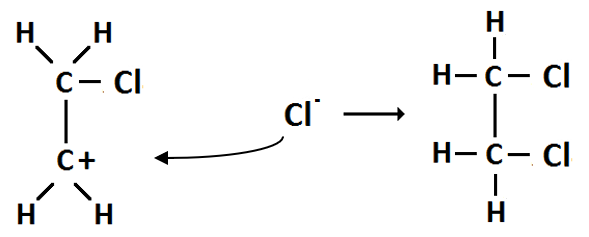
Step 2: Heterolytic fission — the Cl2 molecule splits into ions Cl+ and Cl-

Step 3: Carbonium ion formation — the Cl- ion forms a covalent bond with one of the carbon atoms, leaving the other carbon with a positive charge.
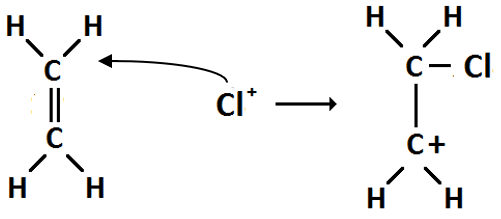
Step 4: Ionic addition — the carbonium ion is then attacked by the Cl- ion forming 1,2 chloroethane.