Question
- Leaving Certificate Physics (Higher) 2021: Section B Q6
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a) Define acceleration. Hence derive the expression v = u + at.
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity:
This can be expressed as: 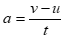
we can rearrange to give: 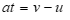
And therefore: 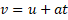
(u = initial velocity, v = velocity after time t, a = acceleration, s = displacement, t = time)
(b) A ball is kicked with an initial velocity of 20 m s —1 at an angle of 50° to the horizontal. Calculate the horizontal distance it travels in 1.2 seconds.
We can use a triangle to find the horizontal component of the velocity, VH:
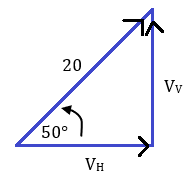
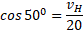
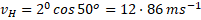
Carrying out a simple distance-speed-time calculation allows us to find the horizontal distance, d, travelled in 1.2 seconds.
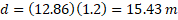
(c) State the laws of equilibrium for a set of co-planar forces.
Laws of equilibrium:
- The sum of the forces in any direction equals the sum of the forces in the opposite direction.
- The sum of the moments about any point is zero.
(d) State an expression for the acceleration due to gravity at a distance of 2R above the surface of a planet of mass M and radius R.
Following the equation:
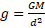
We can say that the acceleration due to gravity at a distance of 2R above the surface (where d = 3R) is given by: 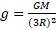
or
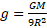
(e) Two different types of thermometer can give different readings when placed in the same environment. Explain why this happens.
Due to variations within thermometric properties, even well calibrated thermometers can give different readings at the same temperature (when that temperature is neither 0 °C or 100 °C)
The Celsius scale is based on the idea that a thermometric property will vary in a linear manner between the two fixed points used (the freezing and boiling points of water). In most situations this assumption is reasonable but it may not be entirely valid and this can cause the effect described here.
(f) Draw a labelled diagram to represent the second harmonic of a stationary wave in a pipe that is open at both ends.
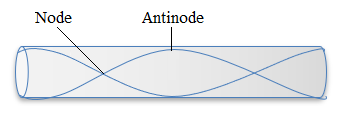
(g) Calculate the sound intensity 6 m from a loudspeaker of power 20 mW.
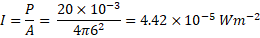
(h) List two primary colours of light. What colour of light is produced when equal intensities of these two primary colours are mixed?
Red and green are primary colours of light. When combined in equal intensities, they produce yellow light.
(i) Distinguish between earthing and bonding in domestic electricity.
All metal appliances should be earthed. This means they should have a third wire connecting them directly to earth. If a fault develops, the current will flow to earth, rather than through the next person who touches the appliance.
Also, all metal surfaces used near water (pipes, taps, etc.) should be bonded. That is, they should be connected to earth. This is to protect from injury should any part of them become connected to a power supply.
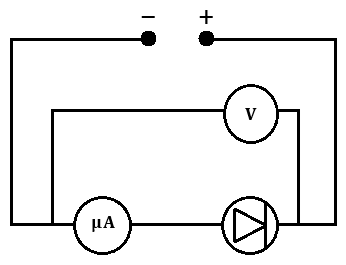
(j) Draw a circuit diagram to show how voltage and current are measured for a diode in reverse bias.
(k) Carbon —14 undergoes nuclear decay. The daughter nucleus is nitrogen —14. Write a nuclear equation for this decay.
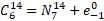
(l) In terms of how they interact with the neutrons in a fission reactor, distinguish between a moderator and a control rod.
The moderator slows down neutrons emitted during fission so that they are travelling at the speed where they are most likely to cause nuclear fission should they hit the nucleus of an atom of, say, U-235.
Control rods absorb emitted neutrons so that they will not go on to cause fission in another nucleus. If fully deployed, they cause the reaction to die out.
