Question
- Leaving Certificate Biology (Higher) 2020: Q12
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
(i) Heredity is the passing of characteristics from parents to offspring by means of genes.
(ii) Mendel’s Second Law of Independent Assortment: At gamete formation, either one of a pair of factors for a particular characteristic is equally likely to combine with either one of another pair of factors for a different characteristic.
(b)
(i) DNA profiling makes a unique pattern of bands from the DNA of one person, which can be compared to and distinguished from the DNA of another person.
Genetic screening uses DNA profiling techniques and adds a radioactive probe to a person’s DNA. This probe only attaches to normal genes, thus indicating when abnormal genes are present. In this way inherited conditions are diagnosed.
(ii) Stages of DNA profiling:
- Stage 1: The DNA is released from the nucleus of the cells.
- Stage 2: The DNA is cut with restriction enzymes leaving fragments of varying lengths.
- Stage 3: DNA fragments are separated by passing an electric current though it. This is called electrophoresis.
- Stage 4: The pattern of bands created is compared to the pattern of DNA from another source.
(iii) DNA profiling can be used for:
- Paternity testing
- Forensic comparison of samples at a crime scene.
(iv) Identical twins have the same DNA profile because they both came from the same zygote and therefore, have identical genes.
(c)
(i) Alleles are alternate forms of the same gene.
Incomplete dominance means neither allele is dominant or recessive with respect to the other. The heterozygous genotype produces an intermediate phenotype.
Homozygous means that both alleles for a characteristic are the same, e.g., TT or tt.
Phenotype is the physical appearance of an organism.
(ii)
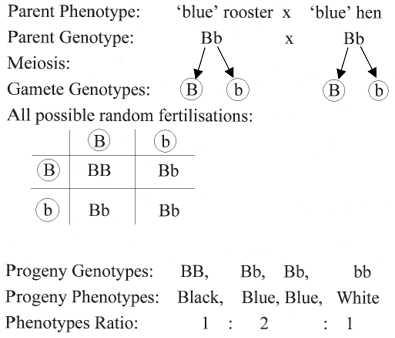
(iii) The phenotype ratio would be 3 Black: 1 White
