Question
- Leaving Certificate Biology (Higher) 2022: Q15
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
(i) Excretion: the removal of the waste products of metabolism from an organism.
Homeostasis: the ability of an organism to maintain a constant internal environment.
(ii) Excretory organ in plants: The leaf.
(b)
(i) It provides protection from damage.
(ii) A: Cortex
B: Medulla
C: Pelvis
(iii) Filtration occurs in part A (the cortex).
(iv) The high pressure allows ultrafiltration to occur. Small molecules such as water, salts, glucose and urea are pushed out of the plasma into the Bowman's capsule because of this pressure.
(v) They allow for: (Only two reasons are required.)
- Reabsorption of water, glucose, amino acids, vitamins and some salts from the PCT into the blood
- Reabsorption of water and salts from the Loop of Henle into the blood
- Reabsorption of varying amounts of water and salts from the DCT into the blood for the fine tuning of these substances
- Secretion of ions out of the blood into the DCT to control blood pH.
(vi) When the body has too little water the hypothalamus causes the pituitary gland to release ADH, which travels in the blood to the kidneys. ADH causes the walls of the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct to become more permeable to water. More water is reabsorbed from these tubes back into the blood and a small volume of concentrated urine is formed. When the body has too much water, the release of ADH is prevented. Extra water is not reabsorbed at the distal convoluted tubule or the collecting duct. A larger volume of dilute urine is formed.
(vii) Structure: Ureter
(c)
(i) Process: Osmosis
(ii) Transverse section of a root:
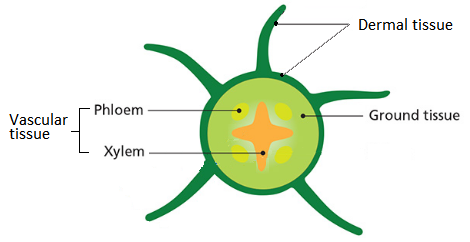
(iii) Scientists: Dixon and Joly
(iv) Upward movement of water in plants:
- Water molecules stick to each other due to hydrogen bonding. This is called cohesion.
- Water molecules stick to the side of the tiny xylem tubes. This is called adhesion.
- Transpiration creates a ‘pulling force’ or tension on the column of water molecules from the top of the xylem.
- Due to cohesion, this lifts an entire column of water from leaf to root.
- Adhesive forces stop the column from breaking.
- This pull lasts as long as transpiration occurs.
