Question
- Leaving Certificate Biology (Higher) 2022: Q11
- Back to the question >
Answer
(a)
(i) Any of the following precautions:
- Tools are flamed in the Bunsen Burner before and after working to prevent contamination.
- Wash the bench with disinfectant before and after working to prevent contamination.
- Wear a lab coat and gloves to prevent contamination.
(ii) Asepsis means the removal of all unwanted, pathogenic microorganisms.
Sterility is the complete absence of any microorganisms.
(b)
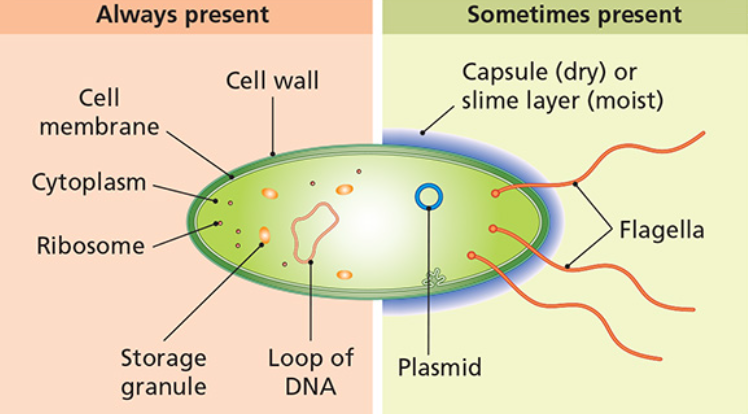
(i) Typical bacterial cell
(ii) Endospore formation:
- The DNA strand of a parent bacterium replicates.
- This produces one cell with two identical strands of DNA.
- The cell elongates with a DNA strand located at each end.
- When times are very harsh, one of the DNA strands is surrounded by a tough walled endospore.
- The parent cell breaks down and the endospore remains dormant until favourable conditions return.
(iii)
1. (Any two of the following harmful bacteria:)
- E. coli
- Salmonella
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus
- Helicobacter pylori
- Vibrio cholerae
2. Antibiotics are chemicals that are produced in microorganisms, which stop the growth or kill other microorganisms without damaging human tissue
3. (Any of the following reasons:)
- Over-prescribing of antibiotics
- Prescribing of antibiotics for viral infections
- Patients not finishing their antibiotics
- Use of antibiotics in farm animals.
(c)
(i) (Any two of the following factors:)
- Temperature
- Oxygen concentration
- pH
- External solute concentration
- Pressure.
(ii)
Temperature
- Low temperatures inhibit growth as the bacterial enzymes are not working at their optimum rate.
- High temperatures will denature the enzymes and kill the microorganism.
- Optimum temperature is 20-30 oC.
Oxygen concentration
- Most bacteria are aerobic and thus, require oxygen for respiration.
- The rest are anaerobic, either facultative or obligate.
pH
Most microorganisms grow at pH 7 but some are found in very high pH environments and very low pH environments.
External solute concentration
High external solute concentration causes water to leave the bacterial cell by osmosis, which kills the bacterium.
Pressure
High pressure will break the bacterial cell wall.
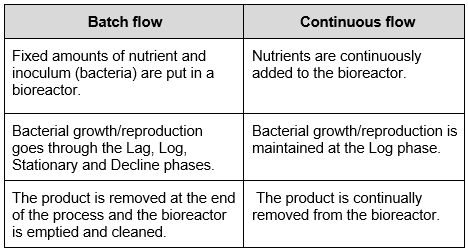
(iii)
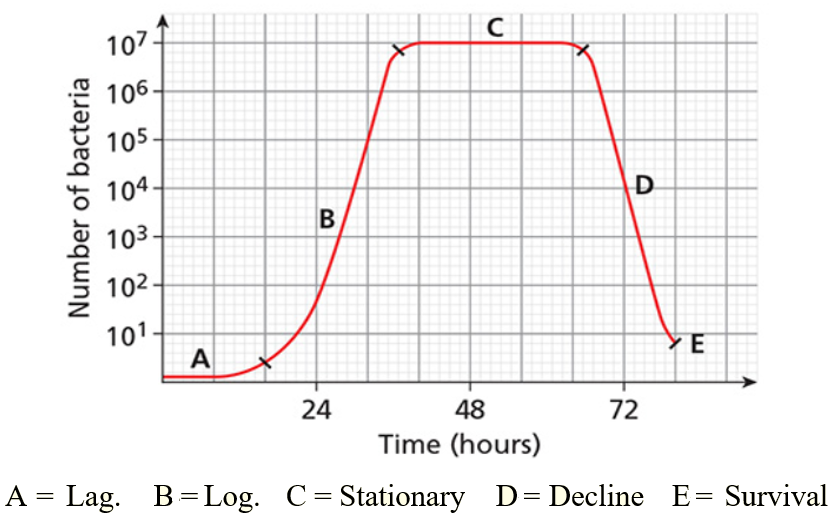
(iv) Growth Curve